Fatty liver disease, new in treatment.
Fatty liver disease, new in treatment, what you didn't know...
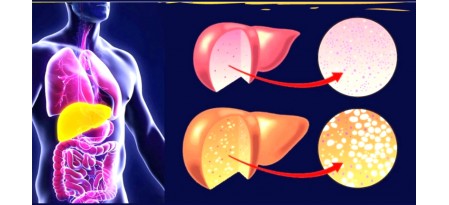
What is fatty liver disease?
Who is at risk for fatty liver disease?
How to define fatty degeneration of the liver?
Consequences of fatty hepatosis of the liver.
Nutrition, diet for fatty liver hepatosis.
New in the treatment of fatty liver.
Liver obesity or liver steatosis leads to the death of hepatocytes (liver cells), their replacement with skeletal connective tissue, circulatory disorders in the liver and the development of liver failure .. All this leads to hepatitis and further to cirrhosis of the liver. Hepatosis dramatically increases the risk of developing liver cancer.
Fatty hepatosis is a disease that is almost asymptomatic, but can have extremely severe complications and requires immediate long-term treatment.
For many years, doctors considered steatosis a benign disease, but many years of experience have shown that with this disease, the risk of cardiovascular complications, diabetes, cirrhosis, fibrosis, liver cancer and all the risks associated with it increases dramatically.
Who is at risk for obesity?
1. The risk of developing fatty liver disease is higher if you have metabolic syndrome. A distinctive feature of which is obesity in the abdomen, hormonal and metabolic disorders.
"If you have a waist circumference of more than 94 cm in men and 80 cm in women, you need to check the liver on ultrasound, you are at risk!"
2. But even quite slender people can develop fatty liver hepatosis, especially if the level of blood triglycerides is elevated.
3. People who abuse alcohol are at risk.
4. There are also high risks of developing fatty disease, such as obesity and type 2 diabetes and other hormonal disorders.
5. And even if you have a very slightly elevated blood sugar, you have prediabetes, then you already have very high risks of this disease.
6. According to statistics, women over 40 suffer from this disease a little more often than men.
7. But sometimes a completely healthy person can be found to have fatty degeneration of the liver.
8. And of course, fatty disease can be a hereditary disease with a violation of the cycle of fatty acid oxidation.
How can you tell if you have fatty liver?
Most often, it is determined quite by accident, with an ultrasound of the abdominal organs or MRI.
But it can also be indirectly indicated by an increase in liver enzymes ALT, AST, GGT.
If you often experience heaviness or pain in the right hypochondrium, you should also undergo an ultrasound scan.
How to treat fatty liver disease?
Unfortunately, there is no magic pill that you can take to get well. But, there is something that has been proven to help you. Fortunately, the liver is an organ that is capable of regeneration (recovery) with the right treatment.
The goal of treatment is to reduce the amount of adipose tissue in the liver, and allow normal liver cells-hepatocytes to recover.
In any case, treatment begins with lifestyle changes, which include both a change in diet and an increase in physical activity. And taking certain medications.
The most important thing is to eliminate the cause, if possible. For example, if you are obese, then it is vital for you to lose weight. The same applies to metabolic disorders, type 2 diabetes, bring your sugar to a more or less normal level with diet, metformin, insulin.
One of the main therapeutic measures remains diet and lifestyle changes.
But, I would not call it a diet, since this way of eating should become your norm for life.
Tablets and methods of treatment with fatty degeneration medicines.
Let's see what are the modern methods of treatment for fatty liver disease?
Of the drug treatments, it is recommended, first of all, the appointment of metformin (Glucophage) starting with a dose of 500 mg. a day before meals. After 10 days, you can increase to 1 tablet of 850 gr. in a day. What will Metformin give you?
Thanks to Metformin, tissue sensitivity to insulin increases, the glycemic index decreases, body weight decreases, blood pressure levels decrease, and vascular endothelial function improves in patients with obesity and arterial hypertension. The results of worldwide studies clearly indicate the significant role of metformin in improving the metabolic changes associated with fatty liver disease.
Metformin gradually restores the sensitivity of hepatocytes (liver cells) to insulin and leads to a proven decrease in the production of very low density lipoprotein cholesterol in the liver. Therefore, the patient's risk of cardiovascular complications is reduced.
The second drug that has shown itself well in the treatment of hepatosis is Ursodeoxycholic acid. In Russia, it can be found under the names Ursofalk, Ursosan and Urdoksa and others.
Its excellent properties for the liver include the ability to: resist pathological processes leading to fatty degeneration, relieve inflammation, reduce total cholesterol and lipid levels, and improve liver biochemical parameters. protect cells from toxic damage, have antitumor activity

 WhatsApp
WhatsApp




























-449x205.jpg)




